Hi friends, you are
welcomed in the Civil Allied Gyan. The field engineers are always looking for
how to improve the workability of concrete. Here I have explained about what is
the workability of concrete and the factors affecting workability of concrete
in detail. First we know about what is the workability of concrete.
What is workability of concrete?
What are the factors affecting the workability of concrete?
The workability of
concrete is affected by type of cement, water-cement ratio, mix design ratio,
size shape and grading of aggregates. In addition to these, process of making
concrete mix and the materials involved in concrete mixing also affects the
workability of concrete.
These
factors are briefly discussed below.
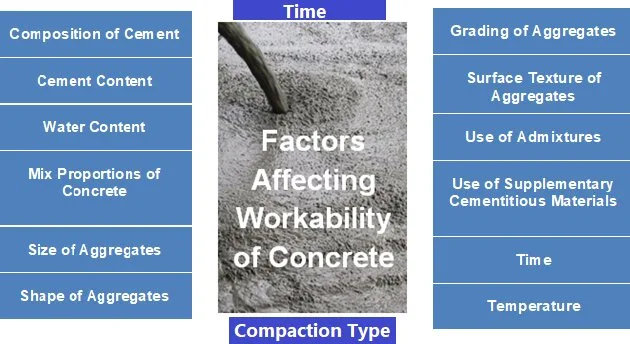 |
| Factors Affecting Workability of Concrete |
Factors Affecting Workability of Concrete
1. Composition of Cement
What cement is made
of, directly affects the workability of concrete. The cement with more fineness
requires more water for same workability compare to the cement with less
fineness. The presence of aluminium oxide (Al₂O₃) and dicalcium silicate (C₂S) in large quantity increases the water
demand to make concrete mix.
2. Cement Content of Concrete
The workability of concrete is also affected by cement content. Higher amounts of cement provide a greater amount of paste in the concrete mix that coats the surface of the aggregates and fills the voids between them. The more cement content helps to reduce friction between the aggregates. This also help in smooth movement of aggregates during mixing, moving, transporting, placing and compacting of concrete.
Also, for a given water-cement ratio, the increase in the cement content will also increases the required water content per unit volume of concrete and finally increases the workability of concrete.
Thus increase in
cement content of concrete mix also increases the workability of concrete.
While the less amount of cement in concrete mix reduce the workability of
concrete.
3. Water Content of Concrete (Water-Cement Ratio)
The water-cement
ratio is the most important factor which affects the workability of concrete.
Generally, a water-cement ratio of 0.45 to 0.6 is used for good workable
concrete mix (without the use of any admixture). As we mentioned above,
increasing in the water-cement ratio increases the water content per unit
volume of concrete and makes the concrete mix more workable.
Note that (only for
nominal mixes):-
Note that (for
designed mix concrete):-
4. Mix Proportions of Concrete (Aggregate-Cement Ratio)
Mix proportion of
concrete is the ratio of fine aggregates and coarse aggregates with respect to
quantity of cement. Generally, this is called the aggregate-cement ratio of
concrete.
Higher the quantity of aggregates w.r.t. quantity of cement nothing other than the less amount of cement. In this condition, very little paste is made for aggregate and so the workability of concrete mix reduces.
The use of less
quantity of aggregates w.r.t. quantity of cement nothing other than the use of
more cement. In this condition, a great amount of pest available for aggregates.
So aggregates have proper lubrications the workability of concrete mix
increases.
5. Size of Aggregates
Surface area of aggregates depends on their size. For the same volume of aggregates, the larger aggregates have less surface area compared to smaller size aggregates.
Lower size aggregates
have larger surface area and so require more water and cement quantity to make
a paste to cover up the entire surface of aggregates. While larger aggregates
have less surface area and require less water and cement quantity to make a
paste to cover up the entire surface of aggregates.
Hence, larger
aggregates are more workable than the lower sizes of aggregates for fixed water
content.
6. Shape of Aggregates
The shape of aggregates is also a factor that affects the workability of concrete. For the same volume or weight, the rounded and subrounded aggregates have less surface area compared to elongated or irregular shaped aggregates.
So it is easy to understand that rounded or subrounded aggregates require less quantity of water than elongated, angular and flaky aggregates for making concrete mix.
So, for fixed water content, rounded or subrounded aggregates are more workable than the elongated or irregular shaped aggregates.
7. Grading of Aggregates
Grading of aggregates is also the most important factor that affects the workability of concrete. Well graded aggregates require less amount of water-cement paste to fill up voids and easily get workability.
If all the sizes are
available in the appropriate percentage in the aggregate, then it is called
well graded-aggregates. A well graded-aggregate has fewer voids in it. And
excess amount of paste will be available to give a better lubricating effect.
Thus the better grading of aggregates increases the workability of concrete.
8. Surface Texture of Aggregates
Surface texture of aggregates is another factor that affects the workability of concrete in the same way as the shape of aggregates.
Aggregates with
smooth surfaces have less surface area than the aggregates of same volume with
rough texture. Roughly textured aggregates show high friction and segregation
tendency. Thus the concrete mix with smooth surfaced aggregates is more
workable than with rough textured aggregates.
9. Use of Admixtures in Concrete
There are many types
of admixtures that are used in concrete for enhancing its properties. There are
some admixtures that are used to increase the workability of concrete.
Plasticizers and
superplasticizers are such type of admixtures which increases the workability
of concrete even with low water/cement ratio. These admixtures reduce the
quantity of water required for same value of slump. So they are called as water
reducing concrete admixtures.
Also air entraining
concrete admixtures are used in concrete mix to increase its workability. It
reduces the friction between aggregates by the use of small air bubbles which
acts as the ball bearings between the aggregate particles.
10. Use of Supplementary Cementitious Materials
There are many
supplementary cementitious materials which are used with cement to improve the
quality of fresh concrete. Fly ash, fibers, silica fume and slag cements are
commonly used supplementary cementitious materials.
Fly ash is a
supplementary cementitious material that is used to improve the workability of
concrete by reducing the water content required for same degree of workability
or slump value. While synthetic fibers or steel are used to reduce the
workability of concrete as it makes the movement of aggregates harder by
reducing the lubricating effect of cement paste.
The use of silica
fume can increase or reduce the workability of concrete on the basis of its
quantity. The use of silica fume in concrete at a low replacement rate can
improve the workability of concrete. But it can reduce workability of concrete
when added at higher replacement rates. Silica fume are used as pumping aid for
concrete mix when it is used as 2 to 3% by mass of cement.
The use of slag
cement also improves the workability of concrete but it's effect depends on the
characteristics of the concrete mixture in which it is used.
11. Time
Fresh concrete
stiffens and loses its workability as time passes though it is not exactly
getting set and strength at all. After preparing concrete mix, some water is
absorbed by aggregates, some may be lost by evaporation and some may be spent
for initial chemical reactions. The loss in workability of concrete by time
depends on various factors like:
Initial workability:
If initial workability of concrete is high, slump loss will be greater.
Property of cement:
If alkali content is high and sulfate content is low in cement, slump loss will
be greater.
Moisture content of
aggregate: Dry aggregates absorb more water than usual and so workability of
concrete mix decreases.
12. Temperature
Temperature also affects the workability of concrete. High temperature causes to reduce workability of concrete and to increase slump loss.
Slump loss is less
influenced by temperature in stiff mixes because this type of mix is less
affected by a change in water content.
The workability of
concrete is also affected by compaction type (by hand or machine) and humidity
of surrounding.
Frequently Asked Questions (FaQs)
Q. What is the importance of workable
concrete in construction?
Q. How to increase workability of
concrete?
These days, the most common method to improve the workability of concrete is the use of chemical admixtures. The use of supplementary cementitious materials materials like slag cement has better effects on workability of concrete. But, the positivity of using admixtures like air entraining is incomparable.
It is noted that workability improvement method depends on the type of structure and particular requirement of the concrete performance.
Q. What is unworkable concrete?
Note that:-
Workability and strength of concrete are inversely proportional to each other.
i.e. increasing the workability of concrete decreases the strength of concrete,
which affects the durability of concrete.
Q. What type of concrete should one use?
|
Thanks for reading this article.
Please, don’t forget to share it. |

