What is Sedimentation Method in Aggregate Test?
Sedimentation method
is a gravimetric method for determining the clay, fine silt and fine dust
content, which includes particles up to 20 micron, in aggregates.
 |
| A sedimentation pipette of the Andreason type |
Determination of Clay, Fine Silt and Fine Dust Content in Fine and Coarse Aggregates by Sedimentation Method
Hi friends, you are welcomed in the Civil Allied Gyan. Read here definition, IS code, apparatus, procedure, formula and lab report for determination of clay, fine silt and fine dust content in fine and coarse aggregates as per IS: 2386 Part-3 (1963).
Note:- Differences
in the nature, density of materials or in the temperature at the time of testing
may vary the separation point.
IS
Code for Determination
of Clay, Fine Silt and Fine Dust Content in Aggregates:-
IS: 2386 Part-2 (1963):-
Estimation of deleterious materials and organic impurities in aggregates.
Apparatus List for Determination of Clay, Fine Silt and Fine Dust Content in Aggregates:-
|
Apparatus List |
Specifications |
|
A
watertight screw-topped glass jar |
Dimensions
similar to a 1 kg fruit preserving jar |
|
A
device for rotating the jar about its long axis |
At
a speed of 80±20 rev/min (horizontally) |
|
A
sedimentation pipette of the Andreason type |
Capacity
approximately 25 ml and of the general form indicated in Figure |
|
A
measuring cylinder |
Capacity
1000 ml |
|
A
scale or balance |
Capacity
not less than 10 kg, readable and accurate to 1 g |
|
A
scale or balance |
Capacity
not less than 250 g, readable and accurate to 0·001 g |
|
A
well-ventilated oven |
Thermostatically
controlled, to maintain a temperature of 100°C to 110°C |
Specification
for sedimentation pipette:- Sedimentations apparatus consists
mainly of a pipette fitted at the top with a two-way tap and held rigidly in a
clamp which can be raised or lowered as required and which is fitted with a
scale from which the changes in height of the pipette can be read.
The volume of the pipette A,
including the connecting bore of the tap B, is determined by filling with
distilled water; by reversing the tap, the water is run out into a bottle, weighed
and the volume calculated.
Chemicals:-
A solution containing
8 g of sodium oxalate per liter of distilled water will be taken. For use, this
stock solution is diluted with distilled water to one-tenth (that is 100 ml of
the stock solution is diluted with 1 liter distilled water).
Sampling
the Test Specimen:-
The sample for test will
be prepared from the main sample taking particular care that the test sample has
a correct proportion of the finer material. The amount of sample taken for test
will be in according to the given table.
Table:-
Weight of sample for test
|
Maximum
Size Present in Substantial Proportion in mm |
Approximate
Weight of Sample
for Test in kg |
|
63 to 26 |
6 |
|
20 to 12∙5 |
1 |
|
10 to 6∙3 |
0∙5 |
|
4∙75 or smaller |
0∙3 |
All aggregates should
be separated into fine and coarse fractions by sieving on a 4·75 mm IS sieve
and the two samples (fine and coarse aggregate) so obtained, which will be
tested separately.
Procedure for Determination of Clay, Fine Silt and Fine Dust in Aggregates:-
Method for Fine Aggregate:-
- Take approximately 300 g of the test sample in the air-dry condition, passing through the 4·75 mm IS Sieve. Then weigh the sample.
- Place the weighed sample in the screw-topped glass jar, together with 300 ml of the diluted sodium oxalate solution.
- Fix the rubber washer and cap (care being taken to ensure water tightness).
- Rotate the jar about its long axis, with this axis horizontal, at a speed of 80±20 rev/min for a period of 15 minutes.
- At the end of 15 minutes, pour the suspension into the 1000ml measuring cylinder and wash the residue by gentle swirling and decant150 ml portions of sodium oxalate solution successively, the washings being added to the cylinder until the volume is made up to 1000 ml.
- The determination will be completed as described in common procedure.
Method for Coarse Aggregate:-
- Take approximately 300 g of the test sample in the air-dry condition, passing through the 4·75 mm IS Sieve. Then weigh the sample.
- Place the weighed sample in a suitable container, covered with a measured volume of sodium oxalate solution (0·8 g per liter), agitated vigorously to remove all adherent fine material and the liquid suspension transferred to the 1000 ml measuring cylinder.
- Repeat this process until all clayey material has been transferred to the cylinder.
- The volume will be made up to 1000 ml with sodium oxalate solution and the determination completed as described in common procedure.
Common
Procedure:-
- Mix thoroughly the suspension in the measuring cylinder by inversion and place the tube and contents immediately in their position under the pipette.
- Then gently lower the pipette A until the tip touches the surface of the liquid and then lower it to another 10 cm into the liquid.
- Three minutes after placing the tube in position, fill the pipette A and the bore of tap B by opening B and applying gentle suction at C.
- A small surplus may be drawn up into the bulb between tap B and tube C, but this will be allowed to run away and any solid matter will be washed out with distilled water from E.
- Then remove the pipette from the measuring cylinder. Now its contents will move in a weighing container.
- Any adherent solids are washed into the container by distilled water from E through the tap B.
- Oven dried the contents of the container from 100°C to 110°C at a constant weight, then cool and weigh it.
Calculations:-
The proportion of
fine silt and clay or fine dust is calculated from the following formula:
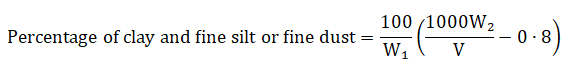
Where,
W₁ = weight of the original sample in g,
W₂ = weight of the dried residue in g,
V = volume of the
pipette in ml and
0·8 = weight of sodium oxalate in one litre of the diluted solution in g.
Note:- No
correction is made for water soluble salts which may be present in the sand,
since the amount of such salts should be small.
Reporting
of Results:-
The clay, fine silt
and fine dust content in aggregate will be reported to the nearest 0·1 percent.
The clay, fine silt or
fine dust content of given sample of fine aggregate is found to be ……. %.
Limits:-
As per IS 383 and
CPWD permissible amount of silt in sand (i.e. fine aggregate) is 3% by mass and
8% by volume respectively.
|
Thanks for reading this article.
Please, don’t forget to share it. |

