What is The Flakiness Index of Aggregate?
The flakiness index of aggregate is defined
as the percentage by mass of particles (stones) in it whose least dimension
(thickness) is less than three-fifths of their average dimension.
Flakiness index of aggregate test is
conducted on coarse aggregates sample to estimate the shape of aggregates.
Thus, evaluation of shape of the aggregate particles,
particularly with reference to flakiness and elongation is necessary.
The flakiness index of an aggregate
sample is found by separating the flaky aggregates by sieving. Flakiness index is
expressed as their weight as a percentage of the weight of the sample tested.
The test flakiness index of aggregate is
not applicable to the materials passing through the 6.30 mm IS test sieve or
retained on the 63.00 mm IS test sieve.
Flakiness Index of Aggregate, Shape Test of Aggregates, IS: 2386 (Part 1)-1963
Hi friends, you are welcomed in the world
of Civil Allied Gyan. Here
I have explained about the test flakiness index of coarse aggregate.
By the help of this you can easily perform
the test flakiness index of coarse aggregate. So please continue to the end
& keep your love and support on me.
Apparatus
Required For The Test Flakiness Index of Aggregate:
- Thickness gauge
- Weighing balance
- Gauging trowel
- Sieves
- IS: 2386 (Part 1)–1963, Method of test of aggregates for formation of concrete
- IS: 383–1970, Specification for coarse and fine aggregate from natural source for formation of concrete
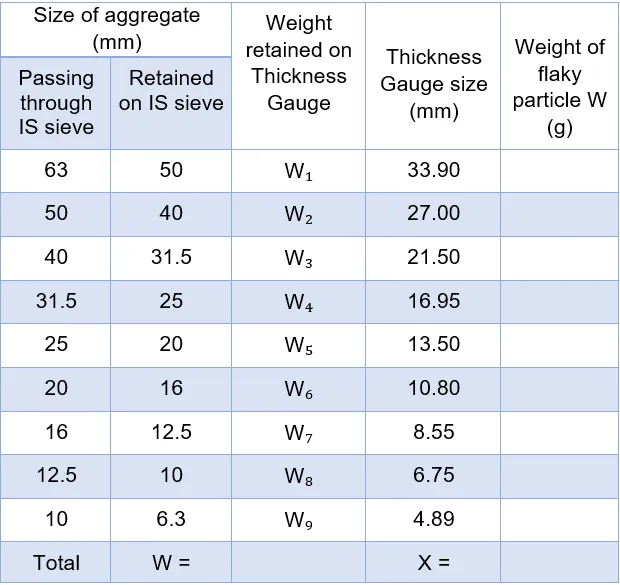
- Sieve the aggregate sample with sieves specified in Table.
- Take sufficient quantity of aggregate to provide the minimum number of 200 pieces of any fraction to be tested.
- Then to separate the flaky materials, gauge each fraction for thickness on a thickness gauge of the pattern shown in Fig or in bulk on sieves having elongated slots.
- The width of the slot used in the thickness gauge or sieve should be of the dimensions specified in column 4 of Table for the appropriate size of material.
- Weigh the total amount of flaky material passing
the gauge to an accuracy of at least 0.1 percent of the weight of the test
sample.
Calculations
and Observations:-
Formula
for flakiness
index of aggregate:

Where,
X = The weight of material passing through the
various thickness gauges and
W = The weight
of aggregate passing and retained on the specified sieves.
Table: Dimensions of Thickness
Results:
Flakiness index of aggregate =
.................
Note:-
Surface texture and aggregate shape influence
the properties of freshly mixed concrete more than the properties of hardened
concrete. Rough-textured, angular and elongated aggregates require more water
to produce workable concrete than smooth, rounded compact aggregates.
Consequently, the cement contents must also
be increased to maintain the water-cement (W/C) ratio. Generally, flat and
elongated aggregate particles are avoided or are limited to about 15 % by
weight of the total aggregate.
Recommended
Values of Flakiness Index and Elongation Index
The aggregate shape tests give only a rough
idea of the relative shapes of aggregates. Flaky and elongated aggregate particles
should be avoided in pavement construction, particularly in surface course.
If the flaky and elongated aggregate particles are present in
appreciable proportions, the strength of pavement construction’s layer would be
adversely affected due to probability of breaking down under heavy loads. Workability of cement
concrete is reduced. IRC recommendations for maximum limits of flakiness index
are as given below.
Sl. No:
|
Type
of pavement
|
Maximum
limits of flakiness index, %
|
1
|
Bituminous
carpet
|
30
|
2 (i)
|
Bituminous
/ Asphaltic concrete
|
25
|
(ii)
|
Bituminous
Penetration macadam
|
|
(iii)
|
Bituminous
surface dressing (single coat, double coats and precoated)
|
|
(iv)
|
Built
up spray grout
|
15
|
3
(i)
|
Bituminous
macadam
|
|
(ii)
|
WBM
base course and surface course
|
The test flakiness index of aggregate is
used to determine the particle shape of the aggregate specimen and each particle
shape being preferred under specific condition.
The significance
of flakiness and elongation index of aggregate are following:
- The degree of packing of the aggregate particles of one size depends upon their shape.
- Due to high surface area to volume ratio, the flaky and elongated aggregate particles lower the workability of concrete mixes.
- For cement concrete types and base coarse construction
and bituminous-construction, the presentence of flaky and elongated aggregate
particles are considered undesirable as they may cause inherent weakness with possibility
of breaking down under heavy loads.
- According to BS-1241, a flakiness index should not exceed 30% irrespective of the aggregate size.
- Maximum permitted elongated index is 35%, 40% or 45% for aggregate size 21/2” – 2”, 11/2” - ¾” and 1/2” - ⅜”.
- Both Flakiness index Elongation Index tests are not applicable to the materials of sizes smaller than 6.3 mm i.e. ¼” sieve.
Read also -



